- What is the Present Simple?
- When do we use the Simple Present tense?
- Affirmative sentences in Present Simple
- Present Simple examples: Short sentences for each subject
- Verbs in Present Simple and the ending “s”
- How to form questions in Present Simple?
- How to form negations in Present Simple?
- When not to use Present Simple?
- Present Simple – online English exercises
- Present Simple – practice with a quiz
The Present Simple is one of the basic tenses in English. We use it to describe events that are regular or routine, as well as to describe actions that are currently occurring. It’s not complicated to make sentences in Present Simple and don’t worry, we will explain all the necessary grammar rules and tell you all about the Present Simple!
The Present Simple tense is usually the first verb tense that we learn in English. It refers to the present and forms the foundation for everyday communication. If you’re preparing for a test on the Present Simple or you simply want to refresh your knowledge, you’ve come to the right place. Today, we will discuss this tense step-by-step, and at the end, we’ll give you a chance to test your knowledge with a simple quiz. So, shall we start? Let’s find out how to use the Present Simple tense!
What is the Present Simple?
The Present Simple tense in English is a verb tense used to express actions that are habitual or generally true. It’s often used for daily routines, facts, and feelings or states of being. The structure of the sentence typically includes the subject followed by the base form of the verb, with an ‘s’ added in the third-person singular. For example, “I play soccer” or “He plays soccer”.
The simple present is the most commonly used verb form in English, accounting for more than half of verbs in spoken English
When do we use the Simple Present tense?
- We use it to articulate our current state or conditions, for example, when indicating where we reside, as in “I live in London.”
- It’s employed to express habitual actions or routines that occur on a regular basis. For instance, “I drink coffee every morning.” We typically accompany these statements with adverbs of frequency such as: always, usually, often, sometimes, rarely, hardly ever, and never, to emphasize the regularity of the action.
- The Simple Present tense is used to state universally accepted truths or facts, like “The sun rises in the east.”
- This tense is also used to describe scheduled or planned future events that occur according to a timetable or routine, as in “The train leaves at 5 pm tomorrow.”
- Finally, the Simple Present tense is used to describe feelings, emotions, or states of being at the current moment, for example, “I feel happy today.”
The verb “to be” in Present Simple
In the Present Simple tense, the verb “to be” behaves a bit differently from other verbs, as it has distinct forms for each personal pronoun. Let’s explore how to use “to be” in the Present Simple tense.
- I am
- You are
- He/She/It is
- We are
- You are
- They are
Adverbs of frequency – How to express the frequency of actions
Adverbs of frequency provide information about the regularity of an action or event. They are often used in conjunction with the Present Simple tense to express how frequently something occurs.
- Always – signifies that action happens 100% of the time, such as “I always eat breakfast at 7 am.”
- Usually – indicates that the action happens most of the time, around 80-90%, as in “I usually go to the gym after work.”
- Often – is used when an action happens approximately 70-80% of the time, like “I often read before going to bed.”
- Sometimes – indicating a 50% occurrence, could be used as in “I sometimes skip lunch when I’m too busy.”
- Rarely and seldom – are used when the occurrence is around 10-20%, such as “I rarely watch TV.”
- Never – denotes 0% occurrence, meaning the action does not happen at all, for example, “I never smoke.”
Note that these adverbs typically go before the main verb, but after the auxiliary verbs and the verb “to be.”
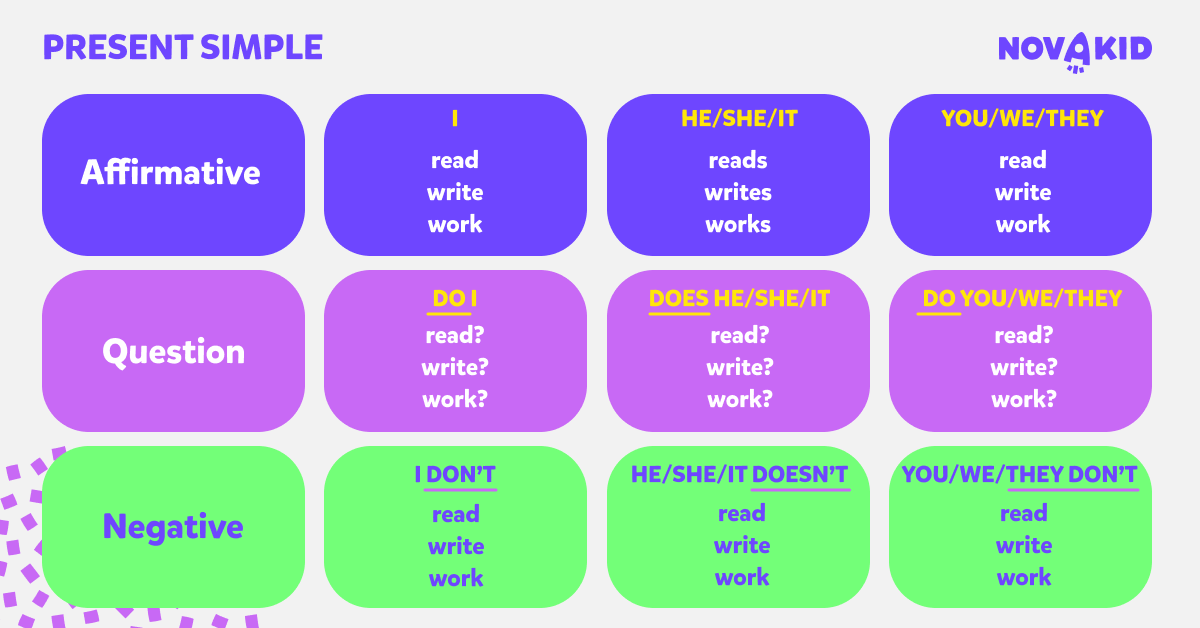
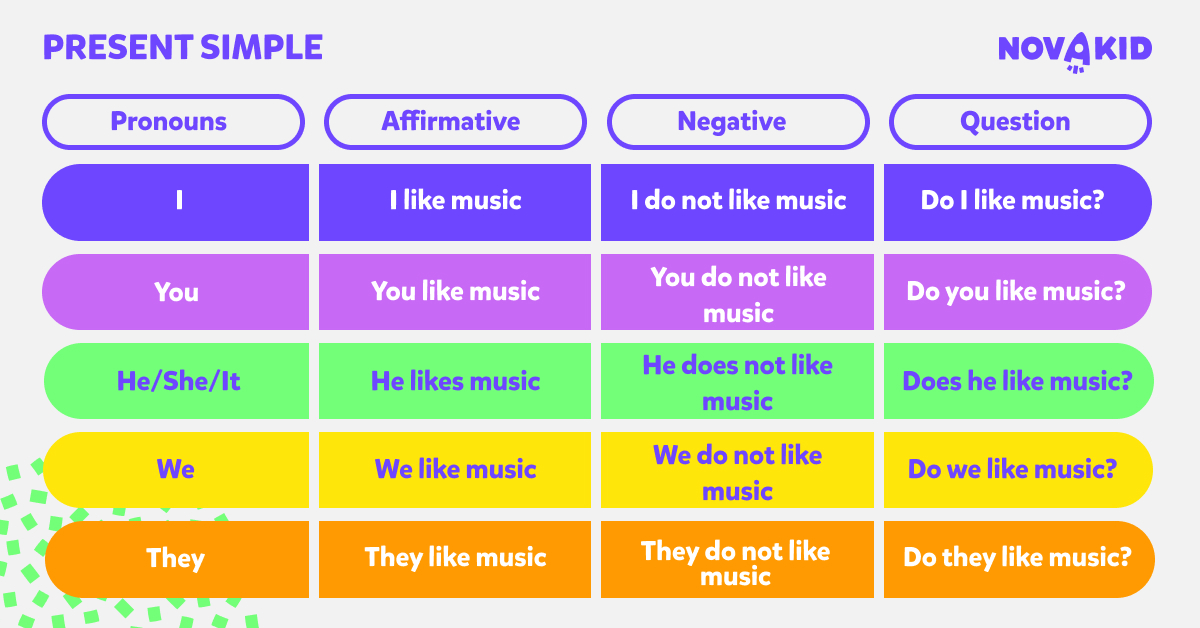
Affirmative sentences in Present Simple
The simplest affirmative sentences in the Present Simple are formed according to the following pattern:
Subject (e.g., I) + verb (e.g., like) + object (e.g., animals) = I like animals.
The only difficulty arises in the third-person singular, when we must add the ending “s” to the verb. Check the graphic below for details.
3rd person singular in Present Simple
In Present Simple tense, when dealing with third-person singular subjects (he, she, it), we typically append an -s or -es to the base form of the verb. However, for all other subjects, the verb remains in its base form without any added endings.
Present Simple examples: Short sentences for each subject
- I play football every Saturday.
- You study English every day.
- He works in a bank.
- She watches TV in the evening.
- It rains a lot in this region.
- We live in a big city.
- You (plural) speak Spanish fluently.
- They eat breakfast at 8 am.

Verbs in Present Simple and the ending “s”
Pay attention to the form of the verb in the third person singular. For example, the verb “to play” in the third person singular is “plays”, and the verb “to watch” is “watches”. And with that, we come to the topic of exceptions in the Present Simple.
Present Simple – Exceptions
The Present Simple tense has two types of exceptions, where we don’t just add “s” in 3rd person singular (he, she, it), but “es” or “ies” to the verbs.
Verbs ending in -s, -x, -z, -sh, -ch + “es”:
- He passes the ball to his teammate.
- She fixes the broken lamp.
- It buzzes loudly.
Verbs ending in a consonant and y + “ies”:
- He studies English every day.
- She tries to solve the problem.
- It flies high in the sky.
How to form questions in Present Simple?
To form questions in the Present Simple in English, use inversion – that is, swap the subject and the verb. For Present Simple questions, add the auxiliary verb “do” or “does” (depending on the subject) at the very beginning of the sentence. “Do” is used for nearly all subjects (I, you, we, they), while “does” is only used for the third person singular (he, she, it).
Questions in Present Simple – Examples
- Do you like coffee?
- Does he play football?
- Do they study English?
- Does she live in London?
- Do we have a meeting tomorrow?
- Does it rain a lot in this region?
Note that in questions with the auxiliary verb “do” or “does”, we no longer use the ending “-s” for verbs in the third person singular.
How to form negations in Present Simple?
To form a negation in Present Simple, add “not” between the auxiliary verb “do” or “does” and the rest of the sentence. “Do not” is used for all subjects (I, you, we, they), while “does not” is only used in the third person singular (he, she, it). You can also use the contracted form – “don’t” or “doesn’t”.
Negations in Present Simple – Examples
- I do not like coffee. / I don’t like coffee.
- You do not speak Spanish. / You don’t speak Spanish.
- He does not play football. / He doesn’t play football.
- She does not live in London. / She doesn’t live in London.
- It does not rain a lot in this region. / It doesn’t rain a lot in this region.
In negative sentences with the auxiliary verb “do” or “does”, we no longer use the ending “-s” for verbs in the third person singular. The same applies to questions.
When not to use Present Simple?
The Present Simple tense is versatile, but it isn’t suitable for every context. Here are some instances when the use of the Present Simple may not be appropriate:
- When describing actions that are happening at the moment of speaking: In English, the Present Simple tense isn’t used to describe actions that are happening right now. Instead, the Present Continuous (or Present Progressive) tense is used.
- When referring to actions that will definitely happen in the future: Though the Present Simple tense can be used for scheduled future events, it is not used for events in the future that are not yet confirmed or planned.
- When expressing a temporary situation: The Present Simple tense generally represents permanent situations, while the Present Continuous is used to talk about temporary situations.
- When discussing past actions or events: The Present Simple is not suitable for discussing events or actions that happened in the past. Different past tenses are used for this purpose.
Present Simple vs Present Continuous
The Present Simple and the Present Continuous tenses are often confused because they both refer to present time. However, they express different types of actions and states.
The Present Simple is used to express habitual actions, general truths, and fixed or scheduled future events. For example, “I swim every morning” (habitual action), “Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius” (general truth), “The bus leaves at 9 am” (fixed future event).
On the other hand, the Present Continuous is used to talk about actions happening at the moment of speaking, temporary situations, or future plans. For example, “I am reading a book” (action at the moment of speaking), “I am living in Paris for a few months” (temporary situation), “We are meeting her at the airport tomorrow” (future plan).
Present Simple vs Future Simple
The Present Simple and Future Simple tenses can also be mixed up, but they are used for different situations.
The Present Simple tense is used for routine activities, general truths, and scheduled future events. For instance, “The store opens at 8 am” (routine/schedule), “Birds fly” (general truth).
However, the Future Simple tense is used to express spontaneous decisions, predictions, or uncertain events in the future. For instance, “I think I’ll go for a walk” (spontaneous decision), “It will rain tomorrow” (prediction), “She’ll probably come to the party” (uncertain future event).
While both tenses can refer to the future, the key difference is that the Present Simple is used for scheduled events and the Future Simple is used for non-scheduled future events.
Present Simple - online English exercises
See if you can now use the Present Simple tense easily with our exercise. Check your knowledge now!
Fill in the sentences with the correct form of the verb in the Present Simple:
- My dad ________ (drink) coffee in the morning.
- We ________ (watch) TV every evening.
- The sun ________ (rise) in the east.
- The cat ________ (sleep) all day.
- The flowers ________ (bloom) in the spring.
- The train ________ (arrive) at 8 o’clock.
- The children ________ (play) in the park.
- I ________ (like) pizza.
- The teacher ________ (teach) us math.
- The dog ________ (bark) at the mailman.
Present Simple - practice with a quiz
See how many points can you score in our Present Simple grammar quiz. Let’s find out!








































I like it!
It is good for beginner
I like it.It is good for me.
For those looking to refine their usage of the Simple Present tense and other tenses, typeng.com is a valuable resource. This free online simulator offers exercises designed to improve your English grammar skills.
I want to learn english
Very nice for beginner.
I like it
appreciates